All about Azure Storage Account
#Azure #StorageAccount #How-To #AzureStorageConfiguration
What is Azure Storage ?
Azure Storage is a Microsoft-managed service providing cloud storage that is highly available, secure, durable, scalable, and redundant. Azure Storage includes Azure Blobs (objects), Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2, Azure Files, Azure Queues, and Azure Tables.
Azure Storage Account is what we create on azure to store any kind of Data (Blob Objects, Files, Table, Queue, )
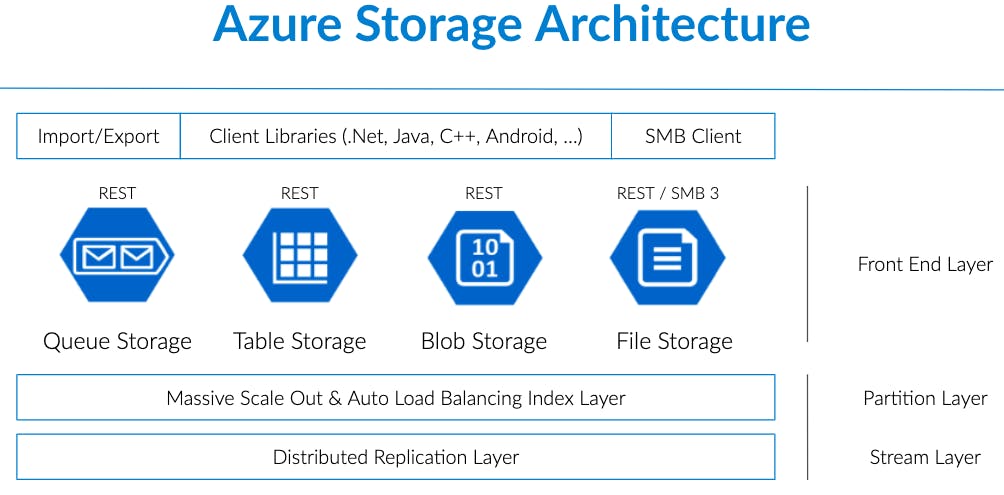
The storage account provides a unique namespace (URL) for your Azure Storage data that is accessible from anywhere in the world over HTTP or HTTPS.
So mainly 5 storage services :
BLOB , QUEUE, FILE , VM Disks and TABLE.

Each has its own uniqueness of usage scenario as per the requirement. Azure Storage consists out of multiple services that are each optimized for a certain usage scenario. They are described in this post, and here is a summary of them:
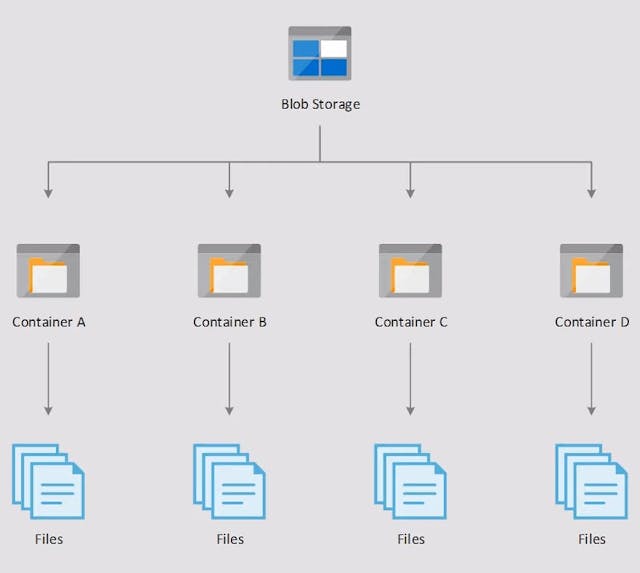
Azure Blob Storage
Useful for storing files, small and large, like audio, video or VHD files
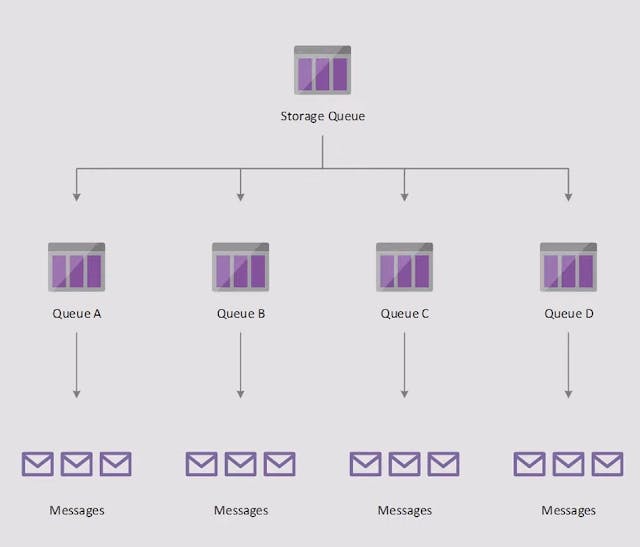
Azure Queue Storage
Meant for storing small messages that are picked up by other applications. Queue Storage can help to decouple your applications
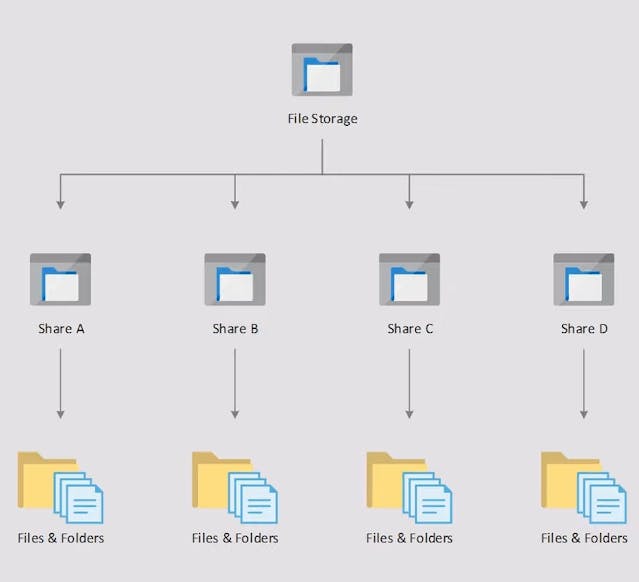
Azure File Storage
Based on the SMB protocol, File Storage is meant to be mounted as a disk in a VM. It is very useful to use for lifting and shifting applications into the cloud
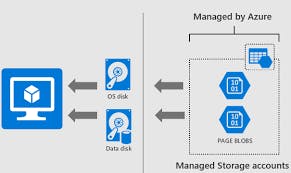
Azure Disk Storage
Disk Storage is optimized for high I/O operations and can be used as a hard disk for a VM, for a server.
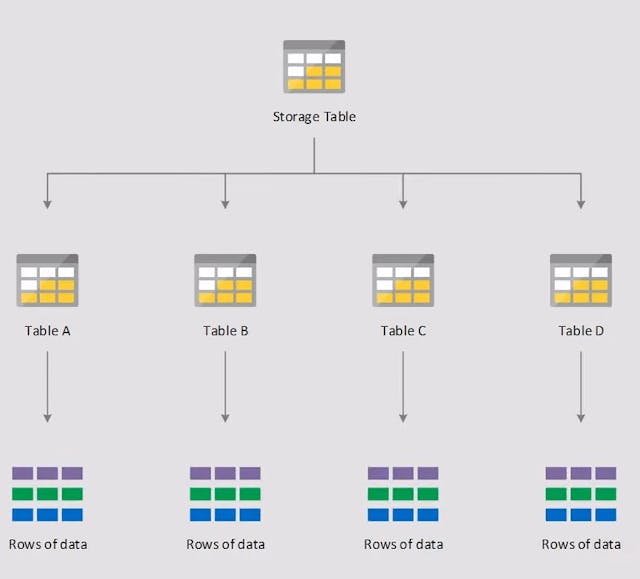
Azure Table Storage
Azure Table storage is a service that stores structured NoSQL data in the cloud, providing a key/attribute store with a schemaless design. Because Table storage is schemaless. Access to Table storage data is fast and cost-effective for many types of applications and is typically lower in cost than traditional SQL for similar volumes of data.
Storage Account Types
General-purpose v2 (GPv2) -
Default, Basic storage account type for blobs, files, queues, and tables. Azure Recommended for most scenarios using Azure Storage + Access Tiers (Cool , Hot, Archive).Premium (Block Blobs, NFS File Shares, Page Blobs) -
Recommended for scenarios with high transactions rates, or scenarios that use smaller objects or require consistently low storage latency
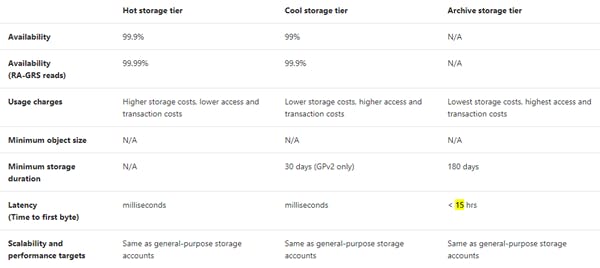
Now, what is Hot/Cold/Archive Blob Tiering in Azure ?
There are three tiers of blob storage in Azure:
Hot
The cheapest to access, but the most expensive to store.
Highly vailable and most durable storage.
Cool
Still low latency, but cheap per GB capacity at higher access rate and stored for at least 30 days. Data in the cool access tier can tolerate slightly lower availability, but still requires high durability, retrieval latency, and throughput characteristics like hot data. For cool data, a slightly lower availability service-level agreement (SLA) and higher access costs compared to hot data are acceptable trade-offs for lower storage costs.
Archive
Extremely cheap per GB storage (~$2.05 per TB per month). The cheapest per GB capacity but it takes up to 15 hours to move a blob back to cool/hot where it can be accessed again.
Now, Storage Account Endpoints,
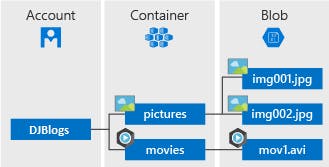
A storage account provides a unique namespace in Azure for your data. Every object that you store in Azure Storage has an address that includes your unique account name. The combination of the account name and the Azure Storage service endpoint forms the endpoints for your storage account.
The following table lists the format of the endpoint for each of the Azure Storage services.
Storage service Endpoint
Blob storage https://<storage-account>.blob.core.windows.net
Azure Files https://<storage-account>.file.core.windows.net
Queue storage https://<storage-account>.queue.core.windows.net
Table storage https://<storage-account>.table.core.windows.net
Storage account billing
Azure Storage bills based on your storage account usage. All objects in a storage account are billed together as a group. Storage costs are calculated according to the following factors:
Region refers to the geographical region in which your account is based.
Account type refers to the type of storage account you're using.
Access tier refers to the data usage pattern you've specified for your general-purpose v2 or Blob storage account.
Capacity refers to how much of your storage account allotment you're using to store data.
Redundancy determines how many copies of your data are maintained at one time, and in what locations.
Transactions refer to all read and write operations to Azure Storage.
Data egress refers to any data transferred out of an Azure region. When the data in your storage account is accessed by an application that isn't running in the same region, you're charged for data egress.
Azure Pricing Calculator for Estimates
How to Create Storage Account ?
We need to follow below steps to “Create storage account”
Go to azure portal and Login > https://portal.azure.com
Search "Storage Account" > Select > Create
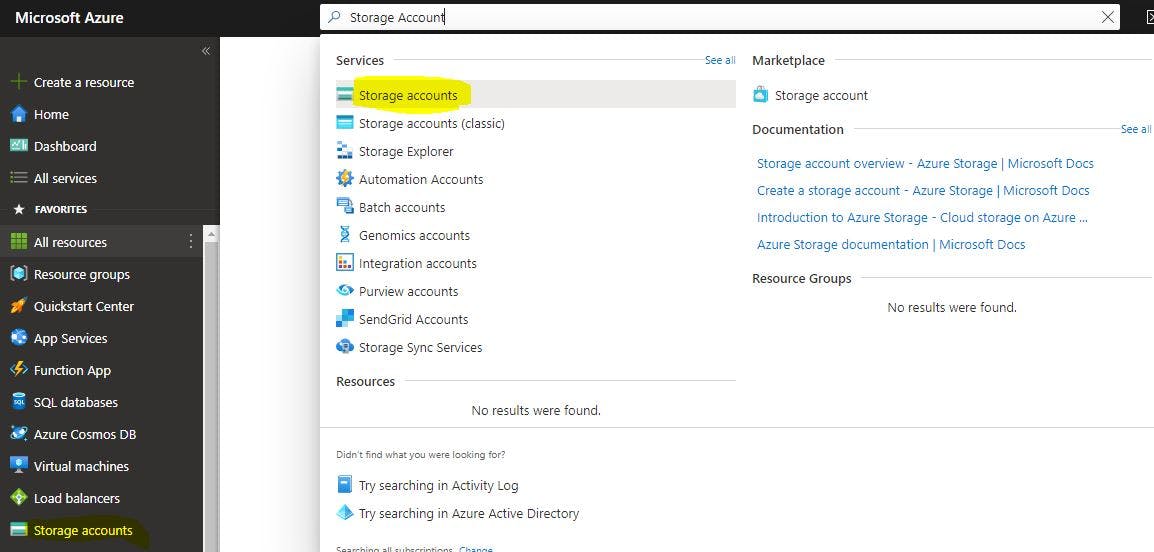
Select Resource Group/Create New
Insert Storage Account Name : It has to be lowercase and unique
Select Performance Tier > Standard (GPv2) or Premium
Select Redundancy: Geo-Redundant (GRS) / LRS / ZRS / GZRS
More on Redundancy
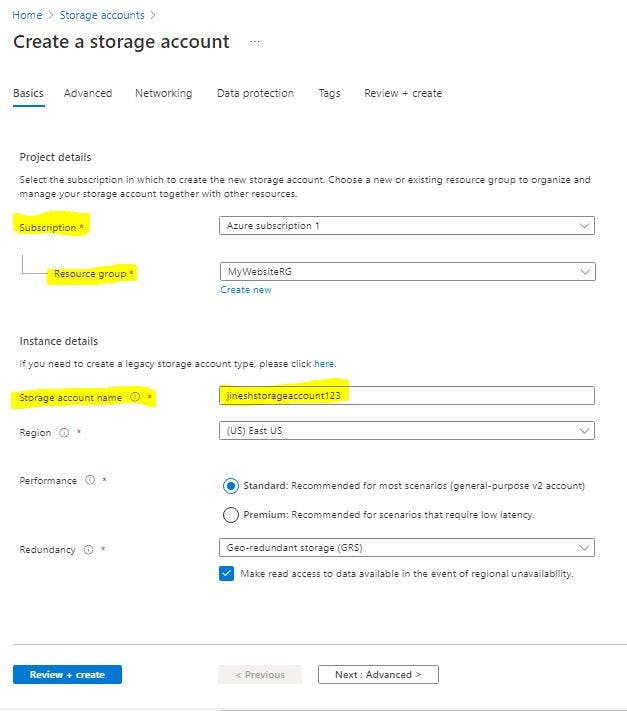
- Next : "Advanced" for Security permissions(REST API, Encryption)
and
Access to storage (Public Access , Storage Account Key Access)
and
Select Minimum TLS (Transport Layer Security) version needed for request to Storage Account.
and
Access Tier : Hot / Cool
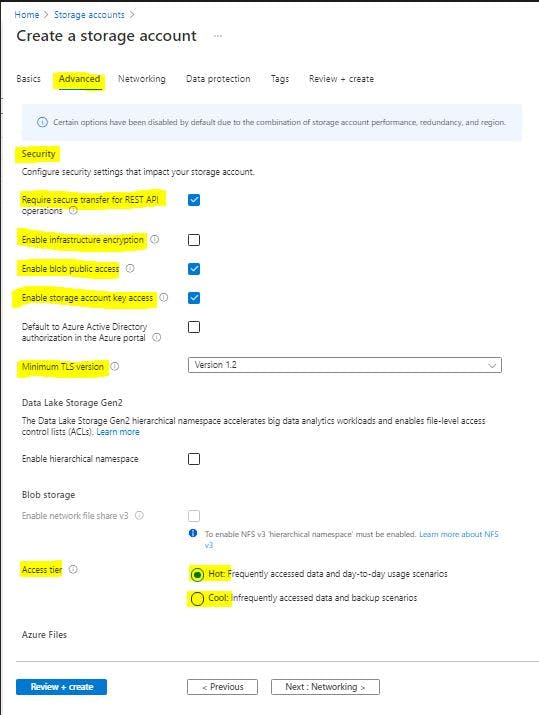
- Next : Networking Connectivity Methods: Public Endpoint (All Networks) OR Public Selected Networks OR Private Endpoint.
And Network Routing : Microsoft Network Routing OR Internet Routing.
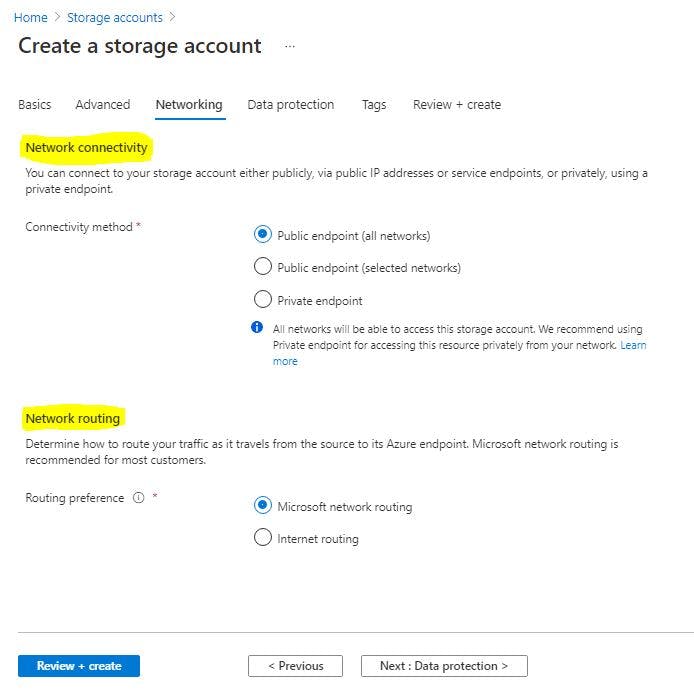
Next: Data Protection
Enable Point-in-Time Recovery , SOFT DELETE and ENABLE VERSIONING , Enable Blob Change Feed.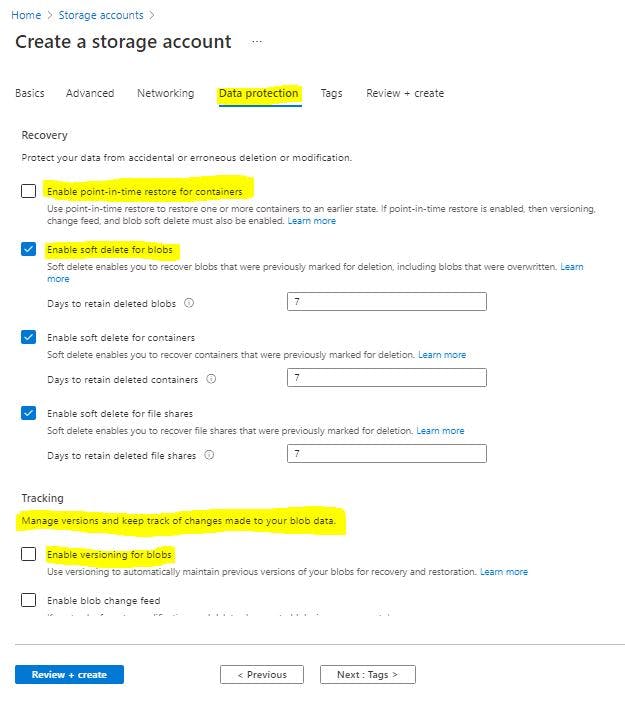
Next: Tags
(It is Best Practice to always Add Tags for Organize and Billing Purposes)Review + Create
Its will show you the Summary of your Configuration and Validation Result.

NOTE: Notice at the bottom, "Download Template for Automation" is the JSON Template to use your selected configuration as a ARM Template to Create for future need just by deploying that Template.
- Create
I hope you enjoy the walkthrough and my All about Azure Storage Account
Feel free to try and Let me know if you have any questions or improvements I can provide.
Thanks for the read. Follow for more Awesome Azure and AWS Content.
Regards,
Jineshkumar Patel

